-
Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
-
Q. What is the definition of male hypogonadism?
- Defect in one of the two functions of the testis
- Sperm production
- Testosterone production
- Defect in one of the two functions of the testis
-
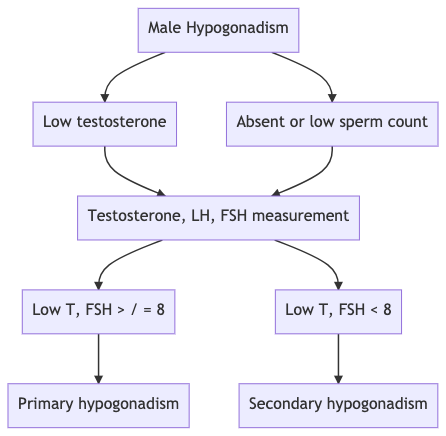
Q. What are the two main groups of causes of hypogonadism in males?
-
-
Causes of primary hypogonadism in males
-
Q. What are major clinical differences between primary and secondary hypogonadism?
- Primary hypogonadism is more likely to be associated with defective sperm production than Leydig cell function
- Primary hypogonadism is more likely to be associated with gynecomastia because of increase FSH and LH increasing the aromatase activity
- FSH >8 IU/l is suggestive of primary hypogonadism
-
Q. Enlist the causes of primary hypogonadism?
- Congenital causes
- Klinefelter's syndrome- most common
- Gonadal dysgenesis
- FSH and LH receptor defect- Leydig cell hypoplasia
- Testosterone synthesis defect
- Cryptorchidism
- Congenital anorchia
- Varicocele
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Acquired causes
- infection- mump orchitis
- HIV
- Testicular tumor
- Drugs – glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide, cisplatin, other chemotherapeutic agents, ketoconazole
- Autoimmune
- Testicular torsion
- Testicular trauma
- Surgery
- Chronic systemic disorder –CRF and CLD
- Environmental toxins
- Radiotherapy
- Surgical orchidectomy
- Congenital causes
-
Q. Why is the timing of testosterone defect important in congenital abnormalities of primary hypogonadism?
- Defect in 1st trimester of pregnancy- male external genitalia would not be appropriately formed – ambiguous genitalia or female external genitalia
- Normal Testosterone in the first trimester but defective in 3rd-trimester micropenis at birth
- Normal Testosterone in utero, Testosterone defect before puberty- absent secondary sexual characteristic, Eunhacnoid proportions, gynecomastia
- Testosterone defect after puberty – normal virilization, gynecomastia, testicular atrophy, reduced libido, infertility
-
**Other congenital causes of Primary hypogonadism in males (other than Klinefelter syndrome) **
-
Q. Which other chromosomal abnormalities are associated with primary hypogonadism in males?
- 46 XY/XO- mixed gonadal dysgenesis
- Yq microdeletion- azoospermia or severe oligospermia
-
Q. What is AZF?
- AZF is a region on the long arm of chromosome Y which is associated with infertility in men
- This produces a condition called Y Chromosome infertility
- There are three regions - AZFa, AZFb, AZFc
- Deletion in AZFa and AZFb produce azoospermia
- Deletion in AZFc produce severe oligospermia - however, enough sperms are produced for sperm extraction using TESE and use for Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
-
Q. What are the features of mixed gonadal dysgenesis?
- Patient will have a Turner like phenotype – e.g.: short stature, etc
- Variable gonads- streak, dysgenetic or normal
- Phenotype ranging from normal female to normal male
- High to intermediate risk of gonadoblastoma hence gonadectomy generally advised
-
Q. What does mutation in LH receptor lead to?
- It leads to Leydig cell hypoplasia
- This produces 46 XY DSD and ambiguous genitalia
-
Q. What are the clinical features of myotonic dystrophy?
- Muscle atrophy
- Hypogonadism
- Detected later in adulthood
-
Q. What happens in congenital anorchia?
- Here, the testicular regression occurs after 20 weeks
- Hence there is normal male external genitalia but absent testis
-
Q. What is Sertoli cell-only syndrome?
- This is a histological syndrome.
- This is typically seen in young males between 20-40 years
- On Semen analysis, they have azoospermia or severe oligospermia
- On Histopathology- the seminiferous tubules are lined with Sertoli cells only, and little or no spermatogenesis takes place
- the testis may be slightly atrophied
- Inhibin B levels may be low
- FSH is elevated with normal LH
- The male is otherwise normally virilized
- The likely etiology is likely to be Y Chromosome infertility due to AZF microdeletions
- Similar situation can also be acquired due to toxins which damage the sperm production
-
Acquired causes of primary hypogonadism
-
Q. Tell me something about mumps orchitis?
- Hypogonadism In mumps orchitis occurs when it occurs in adulthood and not in childhood
- There is swelling and pain of the testis followed by regression
- Seminiferous tubule more damaged, but Leydig damage can also occur
-
Causes of secondary hypogonadism in males
-
Q. What are the features of congenital secondary hypogonadism?
- Normal external male phenotype
- Micropenis at birth
- Normal growth in childhood
- Delayed / absent puberty
- Eunuchoid proportions
-
Q. What are features of eunachoid propotions?
- Arm spam > height by 5 cm
- Pubis to floor > pubis to crown
- This is because of delayed closure of epiphysis due to low testosterone and lack of estrogen
-
Q. What are congenital causes of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
- Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- Part of MPHD (Multiple pituitary hormone deficiencies) – LHX3, LHX4, PROP1, HESX1
- Prader Willi syndrome
- Leptin deficiency / Leptin receptor defect
- Mutation in LH beta and FSH beta
-
Q. What are the acquired causes of secondary hypogonadism?
- Defect at the level of Hypothalamus
- Drugs
- Glucocorticoids
- GnRH analog
- Exogenous sex steroids
- Trauma
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Sleep apnea
- Aging
- Critical illness
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Anorexia nervosa
- Chronic systemic illness
- Drugs
- Defect at the level of the pituitary
- Pituitary adenoma
- Suprasellar mass
- Pituitary apoplexy
- Defect at the level of Hypothalamus