- Credits
- Section Writer: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Section Editor: Dr. Om J Lakhani
- Q. What are the indications for pharmacotherapy in Obesity ?
- Indications for pharmacotherapy in Obesity :
- BMI > 30 kg/m^2
- BMI 27-29.9 kg/m^2 with at least one comorbidity such as:
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Sleep apnea
- Dyslipidemia
- Indications for pharmacotherapy in Obesity :
- Q. What are the goals of therapy while treating with anti Obesity drugs?
- 2 kg weight loss in the first month
- Followed by at least 5% weight loss in the subsequent 3 months
- Q. Which anti Obesity drugs are approved by the US FDA for long-term use?
- Liraglutide
- Lorcaserin- Belviq
- Phentermine – Topiramate
- Buproprion- Naltrexone
- Semaglutide
- Tirzepatide
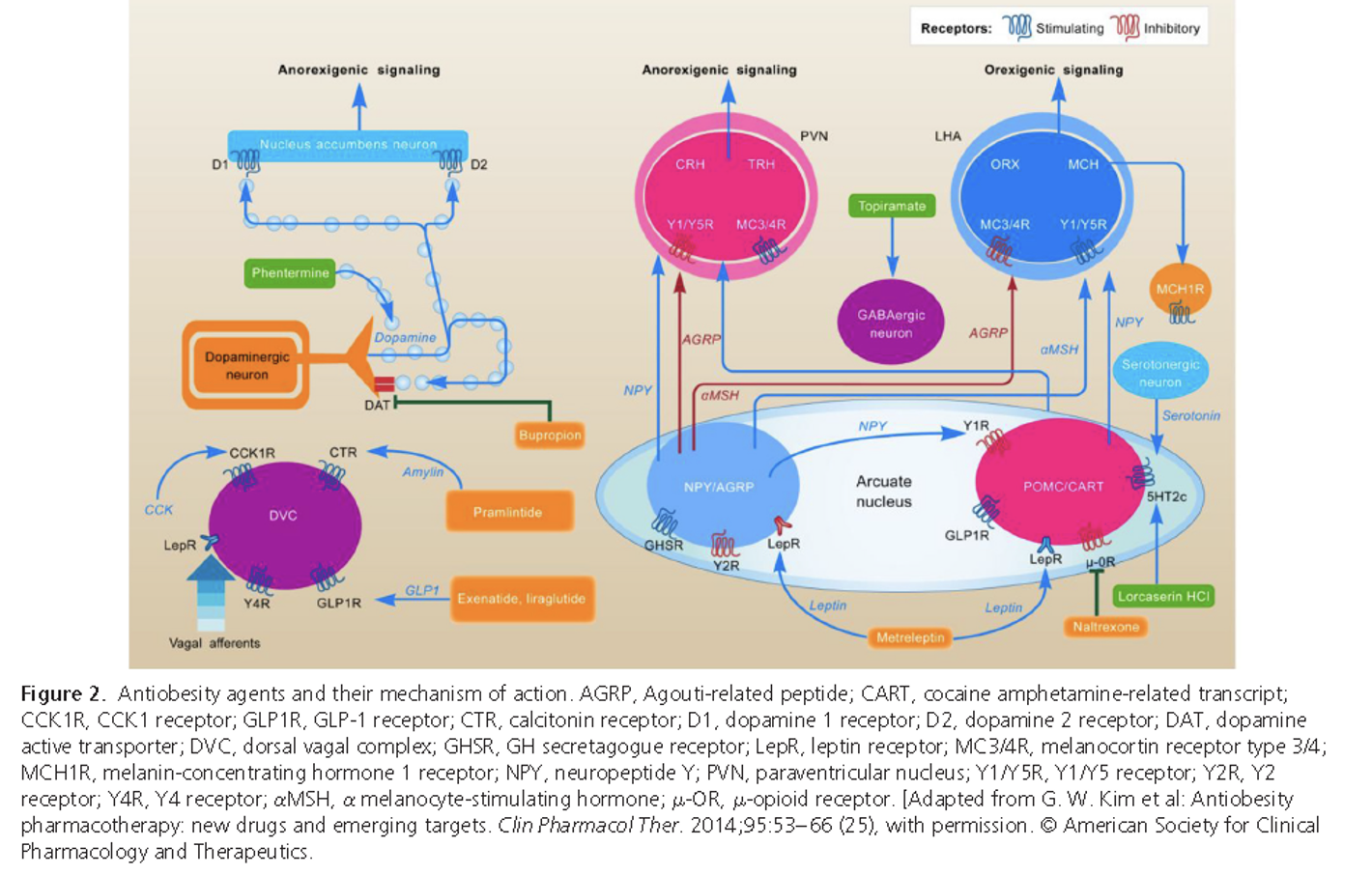
- Q. With a diagram, describe the mechanism of action of various Obesity drugs?
- Q. What are the various levels at which anti-obesity drugs work?
- Hypothalamus
- 5 HT2c receptor agonist- Lorcaserin
- Leptin receptor agonist- metreleptin
- GABA neurons agonist- topiramate
- Opioid receptor antagonist- naltrexone
- Nucleus accumbens
- Dopamine active transporter blocker- Buproprion
- Dopamine release – Phentermine
- Gut
- GLP1 agonist- Liraglutide
- Amylin analogue – pramlintide
- Hypothalamus
- Q. Which drugs are used only for short-term weight management?
- Phentermine
- Diethylpropion
- Benzphetamine
- Phendimetrazine
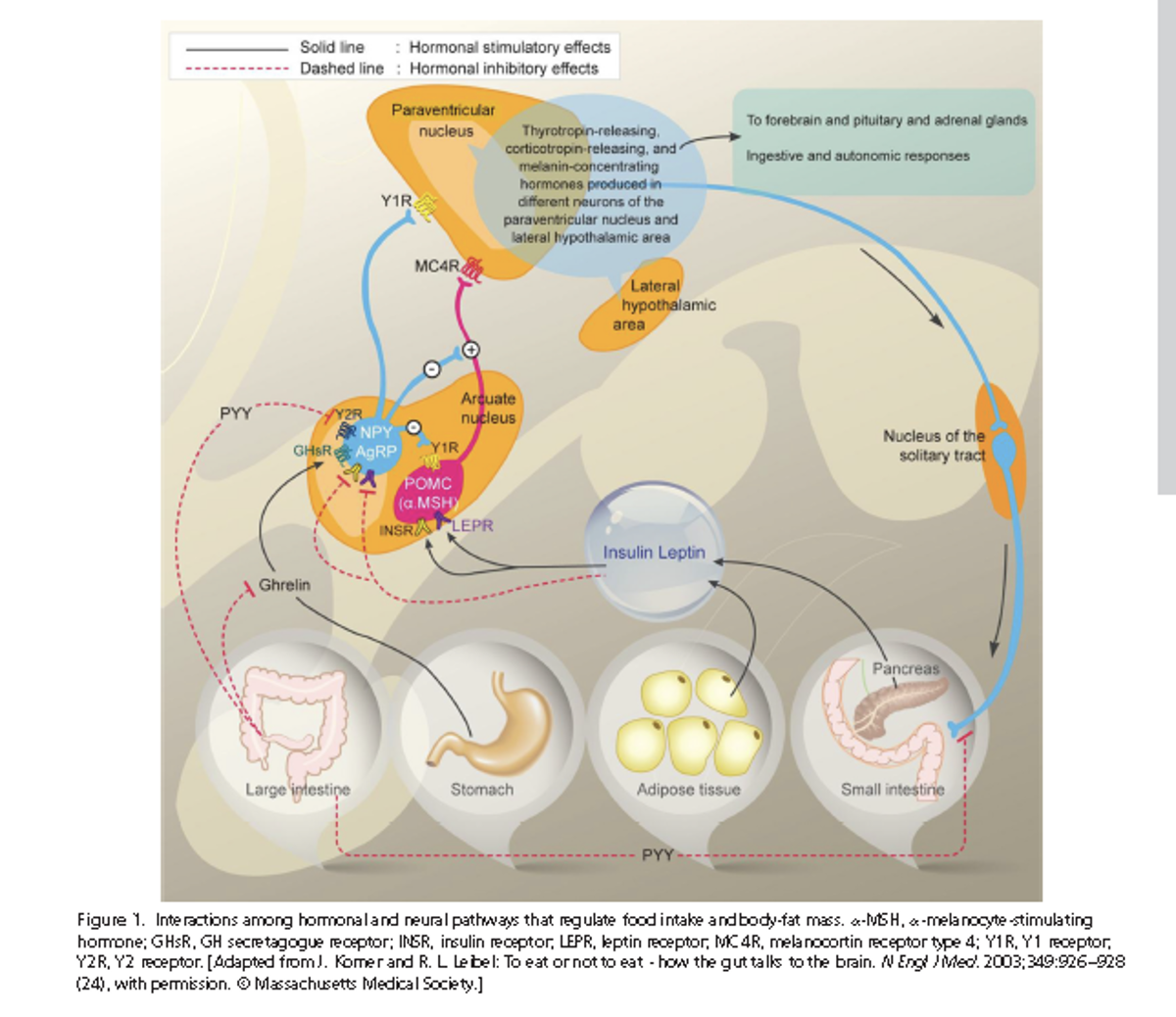
- Q. Give an outline of hormonal and neural interactions in weight management?
- Q. What is the mechanism of action of Orlistat?
- It inhibits pancreatic lipase
- Q. Name 2 rare but potentially dangerous complications of orlistat?
- Rare hepatotoxicity
- Oxalate stones and renal failure
- Q. What is the mechanism of action of Lorcaserin?
- Serotonin receptor 2c agonist
- Q. Activation of which serotonin receptor produces cardiac valvulopathy?
- 5 HT 2B
- Q. What are the contraindications of Phentermine/Topiramate combination?
- Hypertension
- CAD (Coronary Artery Disease)
- Pregnancy- Topiramate is teratogenic
- Q. What is the other side effect of topiramate?
- It is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
- Leads to metabolic acidosis
- Q. What is the composition and dosage of QSYMIA (topiramate/phentermine)?
- Phentermine- 3.75 mg
- Topiramate- 23 mg
- 1 tab x 2 weeks
- 2 tab x 12 weeks
- 3 tab x 2 weeks
- Q. What is the composition and dosage of CONTRAVE?
- Buproprion – 90 mg
- Naltrexone- 8 mg
- 1 tab OD for 1 week
- 1 tab BD x 3 weeks
- 2 tab BD for 8 weeks
- Q. Which antidepressant causes weight loss?
- Buproprion
- Venlafaxine
- Q. What did the XENDOS trial find?
- Reduced incidence of Type 2 diabetes in obese diabetics on Orlistat
- Q. What is the dose of Lorcaserin?
- 10 mg BD
- Q. What did the SCALE study find?
- Liraglutide 3 mg in non-diabetic obese patients
- Led to a loss of 8.4 kg over 56 weeks
- Q. What is the benefit of Orlistat on the lipid profile?
- Causes a reduction of LDL
- This is even higher after adjustment for weight loss
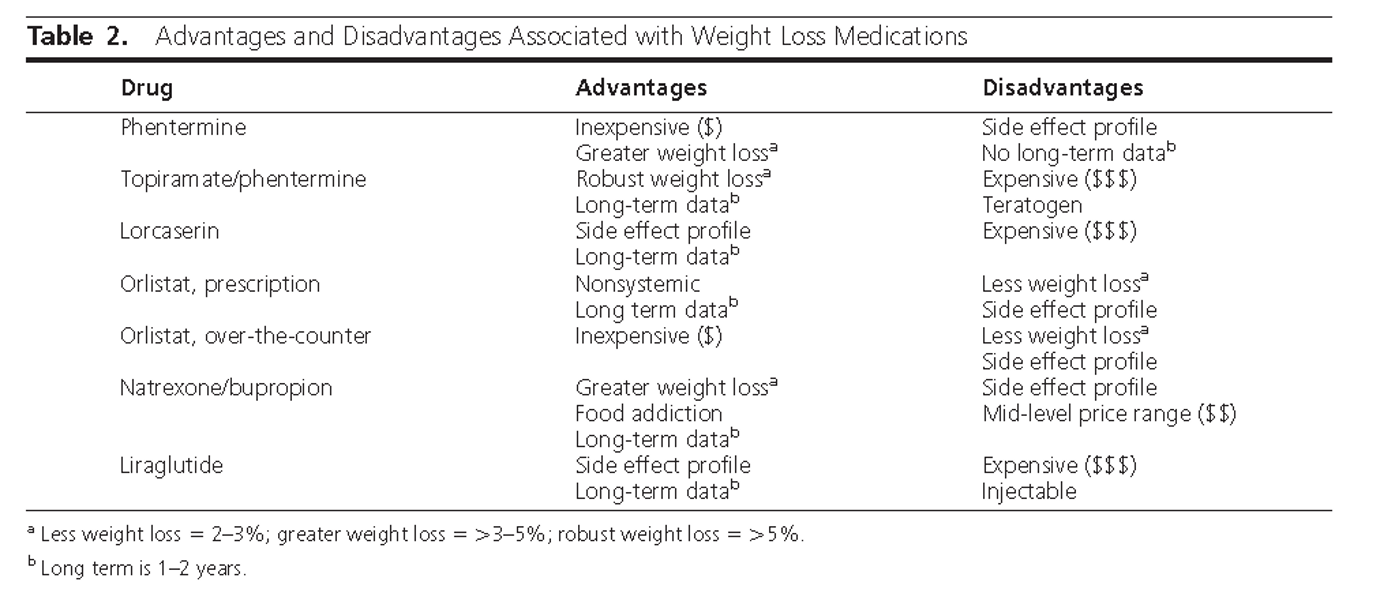
- Q. Give the advantages and disadvantages of various drugs used in the management of Obesity ?
- Q. Apart from topiramate, which other antiepileptic has the potential to be used as an Obesity drug?
- Zonisamide
- Q. Summarize the dose of various drugs used in Obesity management?
- Orlistat- 120 mg TID, 60 min before meals
- Lorcaserin- 10 mg BD
- Topiramate- 23 mg / phentermine – 3.75 mg - BD for 12 weeks
- Buproprion – 90 mg/ Naltrexone- 8 mg – BD-TID for 12 weeks
- Liraglutide- 3 mg subcutaneous
- Semaglutide- 2.4 mg subcutaneous once a week
- Tirzepatide - 5, 10, and 15 mg subcutaneous
- SEMAGLUTIDE
- Q. How do GLP-1 receptor agonists produce weight loss?
- GLP-1 Receptor agonists produce weight loss by slowing gastric emptying to slow glucose entry into the general circulation, inhibiting food intake, reducing abdominal and hepatic fat deposition, improving β-cell function, and increasing insulin sensitivity.
- GLP1 RA acts on the central nervous system, specifically on AgRP (agouti-related peptide), CART (cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript), NPY (neuropeptide Y), and POMC (proopiomelanocortin).
- Q. Do GLP-1 receptor agonists act on the hypothalamus?
- Yes, GLP-1RA acts on the hypothalamus. GLP-1RA has been shown to affect appetite, satiety, hunger, and food preferences, which are all regulated by the hypothalamus.
- Q. What is nucleus accumbens ?
- The nucleus accumbens is a brain region located in the basal forebrain, near the septum. It is part of the mesolimbic reward system and is associated with pleasure, motivation, and reward-related behavior.
- Recent evidence suggests that the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) neuronal projection to the nucleus accumbens core (NAcC) contributes to food intake control.
- Q. What are the series of trials done for obesity using Semaglutide ?
- STEP 1-8
- STEP TEENS
- SELECT TRIAL
- Q. Tell me about the STEP 1 trial?
- The STEP 1 trial was conducted to test the effectiveness of semaglutide at the higher dose of 2.4 mg/week for promoting weight loss in obese or overweight people with related comorbidities, but not diabetes.
- The trial involved 1961 participants and was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in early 2021.
- The findings revealed an average 14.9% reduction in body weight from baseline during 68 weeks of treatment with semaglutide 2.4 mg plus a lifestyle intervention, compared with just a 2.4% reduction in the placebo plus lifestyle intervention group.
- In total, 86.4% of the semaglutide group lost at least 5% of their body weight, and adverse effects were in line with those expected for the medication class.
- The STEP 1 trial demonstrated that semaglutide may be an effective treatment for weight loss.
- Q. What about the STEP 2 trial?
- This compared 1 mg semaglutide to 2.4 mg semaglutide in obese diabetics.
- Q. Then the STEP 3 and 4 trials?
- These were conducted on obese people with comorbidities, but not having diabetes.
- The comparator was a placebo.
- Q. What about the STEP 5 trial?
- This looked at sustained weight loss in non-diabetics.
- Patients were followed up for 2 years.
- Q. What about the STEP 6 trials?
- This was for the Asian population.
- Q. Then STEP 8?
- Compared Semaglutide to Liraglutide.
- Q. What about STEP-TEENS?
- This was done in adolescents between the ages of 12-17 years.
- TIRZEPATIDE
- Q. What is the recent trial for Tirzepatide for Obesity ?
- SURMOUNT-1 trial (Click to open trial details)
- Q. What were the doses used in this trial?
- 5 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg.
- Q. What were the weight loss achieved with these doses?
- 15%, 19%, and 21% respectively.
- Q. How long was the trial?
- 72 weeks.
- Q. What is the SURPRASS-2 trial? (Click to see details)
- Trial comparing Semaglutide to Tirzepatide .
- Doses of Tirzepatide were 5, 10, and 15 mg.
- The dose of Semaglutide was 1 mg.
- Medication was given for 40 weeks.
- Q. What was the HbA1c reduction seen with Tirzepatide ?
- Almost 2% with each of the doses.
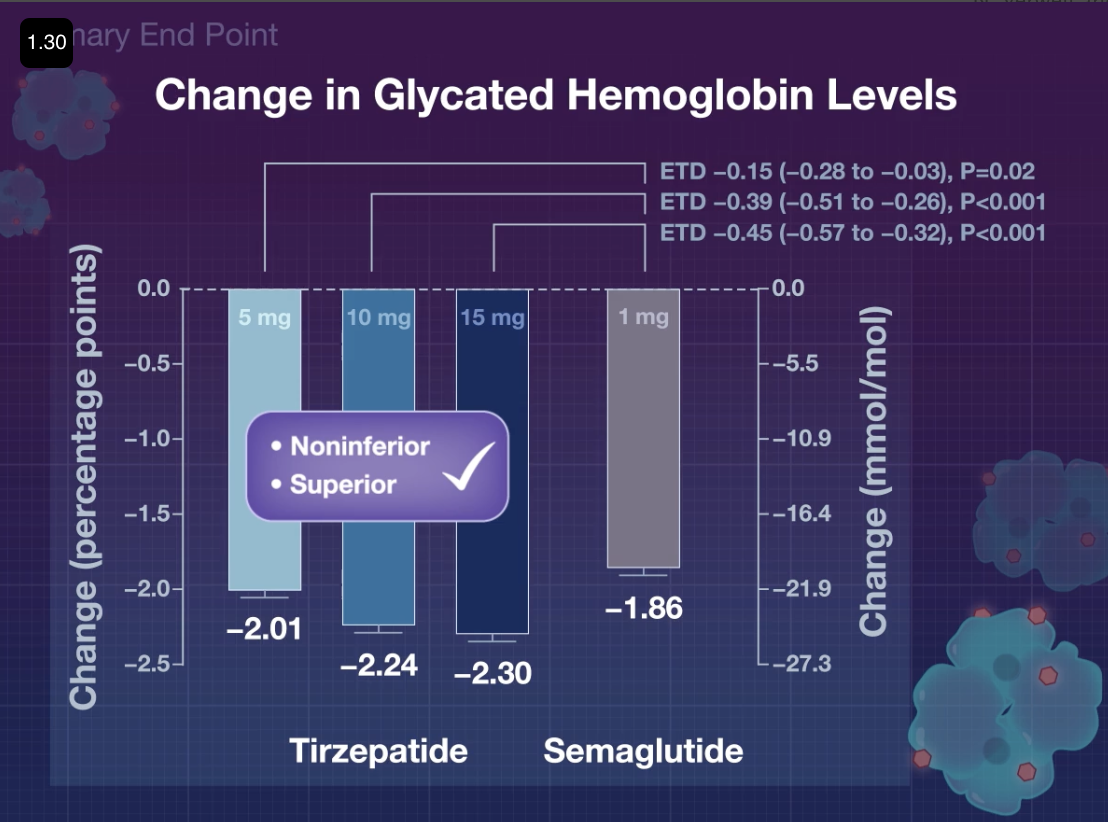
- Q. What was the weight loss seen?
- 7, 9, and 11 kg.
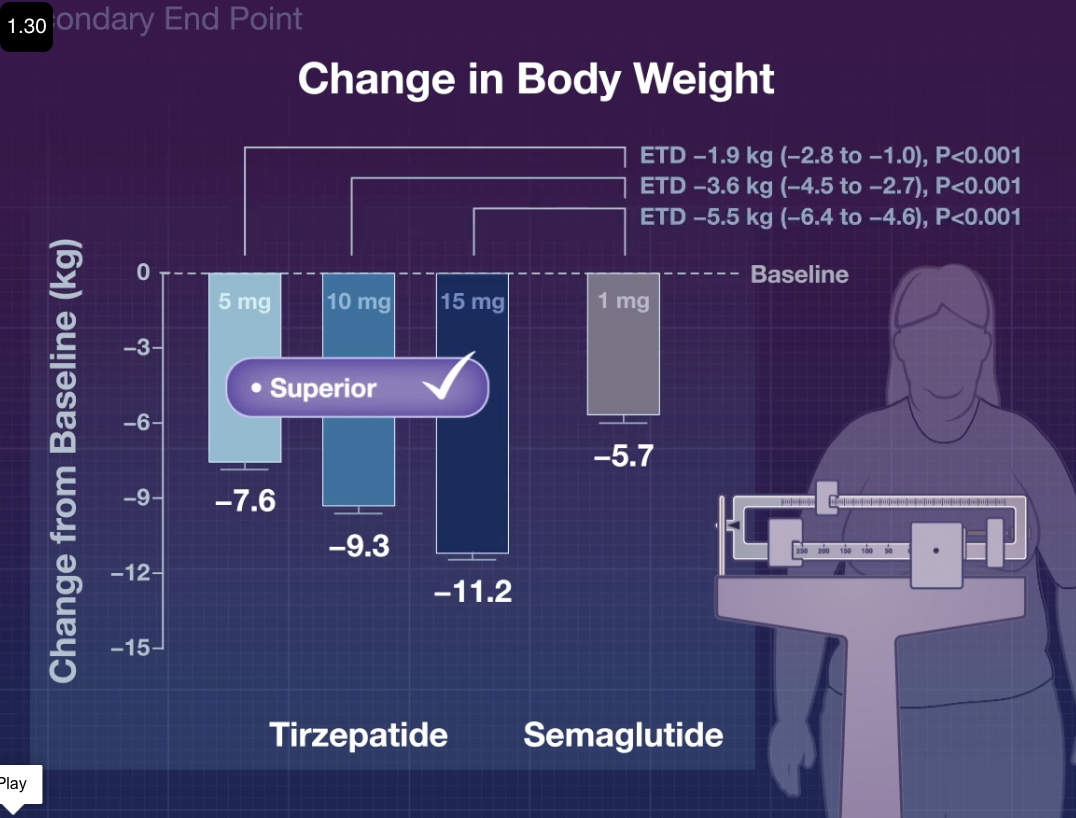
- Q. Which adverse effects were more common with Tirzepatide ?
- Hypoglycemia was seen more compared to Semaglutide .
- Pancreatitis cases were also more.
- NEWER DRUGS
- Q. What are the areas in which potential new drugs for obesity are being developed?
- Potential new drugs for obesity management are currently being researched and developed. These drugs may target the underlying neurohormonal dysregulations that cause weight gain and prevent sustained weight loss. They may also aim to reduce inflammatory and pro-thrombotic markers, as well as chronic disease incidence. Additionally, they may be designed to reduce the anorexigenic hormone leptin and increase the orexigenic hormone ghrelin, in order to create a physiologic environment conducive to sustained weight loss.
- Q. What is cagrilintide?
- Cagrilintide is a peptide analogue developed by Novo Nordisk for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. It is part of a family of GLP1R agonists, which are drugs that act on the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor to improve glycemic control and reduce body weight.
- Q. What is the mechanism of action of cagrilintide?
- Cagrilintide is a GLP1R/GcgR co-agonist that works by stimulating the release of insulin and glucagon, two hormones that help regulate blood sugar levels. It also helps reduce appetite and increase satiety, leading to weight loss.
- Q. What are the indications for injectable semaglutide for Obesity?
- Adults
- BMI ≥ 30 kg/m^2
- BMI ≥ 27 kg/m^2 with at least one weight-related comorbidity
- Pediatric age group
- Age >12 years
- BMI >95th Percentile or greater for age and gender
- Adults
-
Q. Give me the key points from the recently announced SELECT trial?
- The SELECT trial compared semaglutide 2.4 mg to placebo in overweight or obese adults with cardiovascular disease, and semaglutide showed a 20% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events.
- Semaglutide 2.4 mg had a safe and well-tolerated profile in the trial.
- Regulatory approvals for semaglutide 2.4 mg are planned for 2023 by Novo Nordisk.
- The detailed results of the SELECT trial will be presented at a scientific conference in 2023.
- The patients were followed up for 5 years.
- The patients included in the trial were Age >45 years and BMI >27 kg/m^2.
-
Q. What is orforglipron ?
- Orforglipron (LY3502970) is a novel, oral non-peptide glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist being investigated for the treatment of obesity.
-
Q. How much weight loss was seen with Orforglipron ?
- 15% weight loss over 36 weeks with maximum dose
-
Q. What is the dose of orforglipron used in the study ?
- The doses included 12 mg, 24 mg and 36 mg
- The study is called GZGI study and the drug is developed by Eli Lilly